Key Differences Between a Rotary Screw Air Compressor and a Reciprocating Air Compressor
Overview of the Two Compressor Types
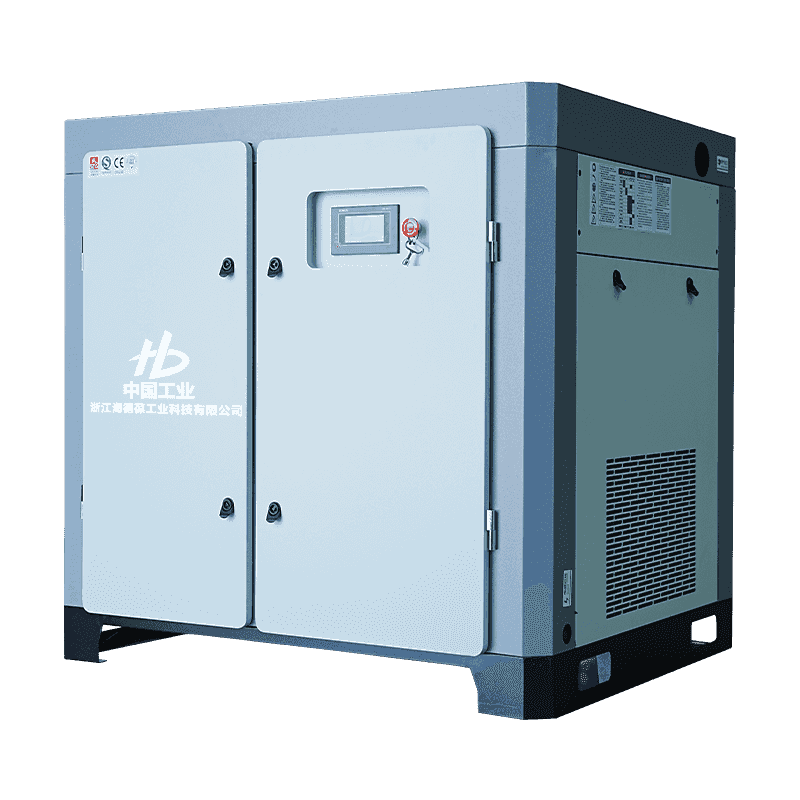
Rotary screw air compressors and reciprocating air compressors represent two core categories of compression technology used in modern industrial environments. Manufacturers such as Zhejiang Haidebao Industrial Technology Co., Ltd., known for producing micro-oil twin screw single-stage compressors, incorporate advanced rotary screw technology that supports long-term, stable, and continuous air output. Reciprocating compressors, on the other hand, rely on piston-driven motion to generate compressed air and are commonly used in smaller-scale or intermittent-demand applications. Understanding the differences between these two technologies helps users select the appropriate equipment for specific operating conditions, especially in industrial sectors that rely heavily on consistent, high-efficiency air supply.
Differences in Working Principles
The core distinction lies in the mechanical process used to compress air. Rotary screw compressors use two intermeshing helical rotors to trap and reduce the volume of air, creating a continuous compression process. This results in smooth airflow without frequent pressure fluctuations. Zhejiang Haidebao Industrial Technology Co., Ltd. integrates micro-oil lubrication into its screw compressor systems to ensure thermal stability and reduce internal wear. Reciprocating compressors work through the linear motion of a piston within a cylinder. As the piston moves downward, air is drawn in, and as it moves upward, air is compressed and discharged. This process creates periodic compression cycles, resulting in fluctuations in flow and pressure. The cyclical nature of reciprocating compressors introduces more mechanical complexity, leading to different performance behavior compared to rotary screw systems.
Structural Differences and Component Layout
Rotary screw compressors typically have a compact structure with fewer moving parts. The rotor set, oil injection system, and cooling components are arranged in a streamlined layout that supports continuous-duty operation. Manufacturers such as Zhejiang Haidebao implement integrated system design to enhance stability and reduce mechanical stress. Reciprocating compressors include pistons, cylinders, connecting rods, valves, crankshafts, and lubrication components. This structure increases mechanical contact points and results in a more complex layout that requires more frequent inspection and adjustment. The structural simplicity of screw compressors allows them to operate with reduced vibration compared to reciprocating models, where the piston motion generates more vibration and noise.
Performance Differences in Air Delivery
Rotary screw compressors provide consistent, continuous airflow, making them suitable for applications that require stable air supply without interruption. The micro-oil twin screw design, used by Zhejiang Haidebao Industrial Technology Co., Ltd., supports efficient heat dissipation and steady thermal conditions, enabling long-duty cycles. Reciprocating compressors deliver air in pulses due to their piston-driven nature. This pulsed airflow may require additional air storage or regulation components in applications where steady output is necessary. While reciprocating compressors can achieve high pressure levels, their intermittent compression makes them less suitable for processes requiring smooth and continuous flow.
Energy Efficiency and Operational Behavior
Rotary screw compressors are generally known for stable energy consumption due to their continuous compression process. The lubrication and cooling systems, such as the micro-oil technology used by Zhejiang Haidebao, help maintain efficient operation with minimal energy waste. Reciprocating compressors tend to consume more energy during startup and may experience fluctuating energy demand based on load cycles. Their mechanical motion introduces additional frictional losses, making them less stable in energy performance during long-term, high-load operation. Screw compressors also benefit from more effective thermal management, which helps maintain consistent operating temperatures and reduces efficiency losses.
Noise and Vibration Comparison
Rotary screw compressors generally operate with lower noise and vibration levels due to the smooth rotational movement of the rotors. Zhejiang Haidebao’s screw compressors are designed to maintain balanced mechanical performance, which contributes to stable acoustic characteristics during operation. Reciprocating compressors generate higher vibration because of the repetitive up-and-down motion of the pistons. This vibration can lead to higher structural stress, increased maintenance requirements, and greater noise output. Sound-dampening measures are often necessary for reciprocating systems operating in enclosed or sensitive environments.
Maintenance Requirements and Durability
Screw compressors usually require less frequent maintenance because of their reduced number of moving parts and continuous lubrication. The micro-oil lubrication system used in Zhejiang Haidebao’s equipment helps maintain stable operating conditions and reduces wear on internal components. Reciprocating compressors require more frequent inspection and component replacement due to their reliance on pistons, rings, and valves. These components experience more direct mechanical stress and wear, making them more maintenance-intensive over time. Maintenance intervals also differ significantly, with rotary screw units offering longer service cycles compared to reciprocating models.
Application Suitability Across Industries
Rotary screw compressors are widely used in manufacturing, chemical processing, automotive production, food handling, and other fields requiring stable, long-term air supply. Zhejiang Haidebao’s products are designed for industrial environments where reliability and continuous operation are priorities. Reciprocating compressors are more commonly used in workshops, small manufacturing units, or applications where air demand is intermittent rather than constant. Their capability to achieve high pressures makes them suitable for tasks such as tire inflation, small-scale pneumatic tool operation, and short-cycle industrial processes.
Comparison Table of Key Differences
The following table summarizes major distinctions between rotary screw and reciprocating compressors for easier reference:
| Aspect |
Rotary Screw Compressor |
Reciprocating Compressor |
| Compression Method |
Continuous rotary compression |
Piston-driven intermittent compression |
| Airflow Behavior |
Stable and continuous |
Pulsed and fluctuating |
| Maintenance |
Lower frequency, fewer wear points |
Higher frequency, more components to maintain |
| Noise and Vibration |
Lower due to smooth rotation |
Higher due to piston movement |
| Industrial Suitability |
Best for continuous-duty applications |
Suitable for intermittent or small-scale use |
Cost and Operational Considerations
Rotary screw compressors typically involve a higher initial investment due to their advanced design and integrated lubrication systems. However, their operational stability and lower maintenance requirements often reduce long-term costs. Reciprocating compressors have a lower upfront cost but higher long-term maintenance expenditures. For companies such as Zhejiang Haidebao Industrial Technology Co., Ltd., the focus on screw compressor technology aligns with industries that prioritize operational continuity, predictable energy usage, and extended equipment lifespan.
Cooling System Reliability in Twin Screw Air Compressors for Continuous Operation
Overview of Twin Screw Air Compressor Cooling Systems
Twin screw air compressors, such as those manufactured by Zhejiang Haidebao Industrial Technology Co., Ltd., rely on precise thermal management to maintain stable and continuous operation. The 10HP micro-oil twin screw single-stage compressor integrates a specialized cooling system that is designed to handle high ambient temperatures and extended operation periods. This system ensures that lubricating oil and internal components maintain optimal temperatures, preventing overheating that could compromise performance or longevity. Effective cooling is essential to achieve stable output and low wear rates during long-term industrial usage.
Design Principles of the Cooling System
The cooling system in a twin screw compressor is designed based on specific operating parameters, including ambient temperature, airflow, and thermal load. Zhejiang Haidebao’s compressors utilize a combination of oil-cooled mechanisms and high-performance coolants to regulate the temperature of the lubricating oil and rotors. Internal baffles and carefully positioned oil channels ensure uniform heat dissipation throughout the system. By maintaining a controlled temperature environment, the cooling system reduces thermal stress on critical components such as the rotors, bearings, and motor, enabling the compressor to operate continuously without degradation.
Impact on Continuous Operation
Long-term continuous operation places significant thermal and mechanical demands on a compressor. Without effective cooling, elevated temperatures can lead to oil breakdown, increased friction, and premature component wear. Zhejiang Haidebao’s twin screw compressors are engineered to handle these challenges by combining efficient oil separation, oil-cooled permanent magnet synchronous motors, and heat-resistant components. This design ensures that even during sustained operation under full load conditions, the system can maintain stable lubrication, temperature, and air output, which is critical for industrial processes requiring uninterrupted compressed air.
Advantages of Micro-Oil Lubrication with Cooling
The integration of micro-oil lubrication with an advanced cooling system provides multiple benefits for long-term operation. The low-pressure, specialized oil separation system minimizes oil carryover while ensuring sufficient lubrication of moving parts. Coupled with an effective cooling mechanism, this setup maintains the viscosity and thermal stability of the oil. As a result, the compressor experiences less friction, lower energy consumption, and reduced maintenance requirements. This combination supports sustained operational performance over extended periods without frequent shutdowns or repairs.
Temperature Management and Motor Protection
Zhejiang Haidebao compressors use oil-cooled permanent magnet synchronous motors, which rely on the cooling system to maintain low temperature rise during operation. The motors have no excitation current, which improves efficiency and reduces starting current, but effective cooling remains crucial to prevent overheating. Proper heat management ensures the motor operates within safe thermal limits, extending the service life of the rotor and bearings. Continuous cooling also contributes to consistent energy efficiency and power factor during long-term operation, maintaining reliable performance in demanding industrial environments.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
An efficiently designed cooling system reduces the likelihood of thermal-related failures and allows for longer maintenance intervals. Regular inspection of coolant levels, oil quality, and heat exchanger performance ensures sustained operation. Zhejiang Haidebao’s focus on integrated design and high-quality components supports minimal downtime. By preventing overheating and maintaining stable lubrication, the cooling system enhances the overall reliability and predictability of the twin screw compressor during prolonged use.
Comparison Table of Cooling System Benefits
The table below highlights the advantages of a well-engineered cooling system in a micro-oil twin screw compressor for continuous operation:
| Aspect |
Effect on Continuous Operation |
| Oil-Cooled Motor |
Maintains motor temperature within safe limits, prolonging service life |
| Specialized Coolant |
Ensures stable lubrication and prevents thermal degradation of oil |
| Internal Baffles |
Promotes even heat distribution, preventing hotspots |
| Oil Separation System |
Reduces oil carryover while maintaining lubrication and cooling efficiency |
| Thermal Management |
Supports consistent performance and energy efficiency under full load |
Application in Industrial Scenarios
The robust cooling system of Zhejiang Haidebao’s twin screw compressors allows them to be used in continuous-duty industrial applications such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and other sectors where stable and uninterrupted compressed air is essential. By maintaining consistent operating temperatures and preventing thermal stress, these compressors provide reliable performance in environments that demand high air quality and stable output.



 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى